An eye examination should be part of everyone’s normal health routine and is an important part of looking after your eyes. Some important reasons to have a regular eye examination and look after your eyes :
How Often Should I Get My Eyes Checked?
It depends in part on your age and also on your eyes and family. If you’ve had eye trouble in the past, or if you’re at risk for developing it (if someone in your family had it), you should see an eye doctor every year. Of course, if you have any problems with your eyes, or notice any changes in your sight, then you should see your opthamologist too.
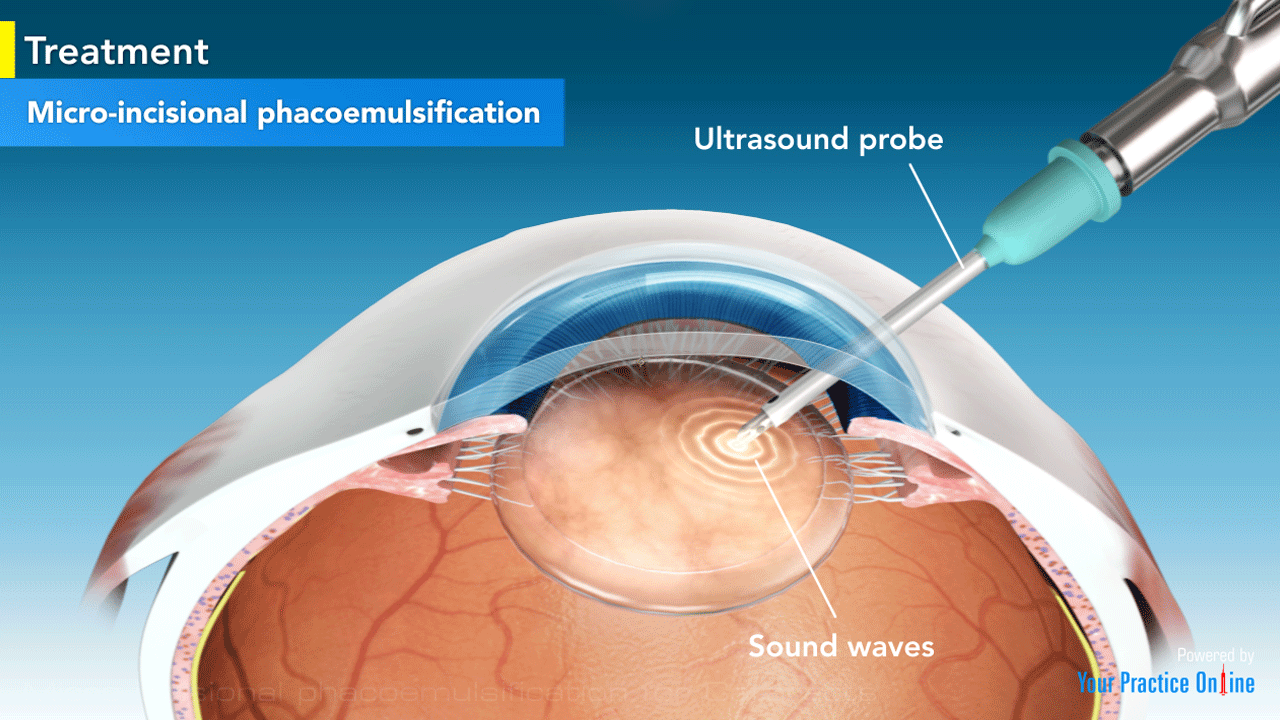
Phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification is a modern cataract surgery in which the eye's internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the anterior chamber.
How a cataract looks ?
In a normal eye, the lens-which lies behind the pupil-is clear (transparent), so the pupil appears black. In an eye with a severe cataract, the cataract clouds the lens. So the pupil may look gray or cloudy.
Incision for surgical instrument is made -
Two small cuts (incisions) are made in the eye where the clear front covering of the eye (cornea) meets the white of the eye (sclera). Next, a small, circular opening is made in the front of the lens capsule to allow access to the cataract. A small surgical instrument (phaco probe) is inserted into the eye.
Intraocular lens (IOL) -
A variety of IOL types are available to replace your natural lens. After the cataract is removed, an intraocular lens (IOL) may be placed inside the lens capsule. The intraocular lens (IOL) takes the place of the eye's natural lens. The incision does not usually require stitches, unless the surgeon decides they are needed.
Retelent Type
Foldable IOL -
They can be placed into the eye through a much smaller incision. These implants have flexible optic lenses made of acrylic or solid silicone. They can be placed into the eye through a self-sealing incision as small as 1/8th of an inch. Through the small incision, the cataract is broken apart with an ultrasound device and gently vacuumed from the eye. These small incisions do not induce significant changes in the patient’s astigmatism seen with larger incisions of the past, thus results are more predictable.
Multifocal IOL -
These IOLs provide both distance and near focus at the same time. The lens has different zones set at different powers. It is designed so that your brain learns to select the right focus automatically.
Toric IOL -
For people with astigmatism, there is an IOL called a toric lens. Astigmatism is a refractive error caused by an uneven curve in your cornea or lens. The toric lens is designed to correct that refractive error.

Lenstar provides highly accurate laser optic measurements for every section of the eye − from the cornea to the retina. With its integrated Olsen formula and the optional Toric Planner featuring the Barrett Toric Calculator, Lenstar supplies the user with latest technology in IOL prediction for any patient.

Glaucoma can begin to develop without noticeable symptoms, the best way to protect your sight from glaucoma is to have regular comprehensive eye examinations to assess your eye pressure, optic nerve health, thinning of the cornea, and other signs of potential problems.
A complete eye exam includes five common tests to detect glaucoma :-
Children experience a variety of eye problems, many quite distinct from adult eye diseases. Pediatric ophthalmologists focus on the development of the visual system and the various diseases that disrupt visual development in children. They have expertise in managing the various ocular diseases that affect children. They are qualified to perform complex eye surgery as well as to manage children's eye problems using glasses and medications. In addition to children with obvious vision problems, children with head turns, head tilts, squinting of the eyes, or preferred head postures (torticollis) are typically referred to a pediatric ophthalmologist for evaluation.

A Squint or Strabismus develops when the eye muscles do not work in a balanced way and the eyes do not move together correctly. This loss of coordination between the muscles of the two eyes leads to misalignment.
Treatment -
Squint does not correct on its own. Treatment of squint should begin as early as possible. Squint treatment for children include muscle exercises, use of prisms in spectacles and surgery to correct squint. Amblyopia therapy may also be required in cases with lazy eye. In order to improve vision, the weakened muscles in the affected eye or eyes must be put to work. Several Squint treatment techniques may be used alone or in combination, depending on the type, severity, and cause of strabismus, including – Eyeglasses or contact lenses may help people who have crossed eyes due to an uncorrected farsightedness.

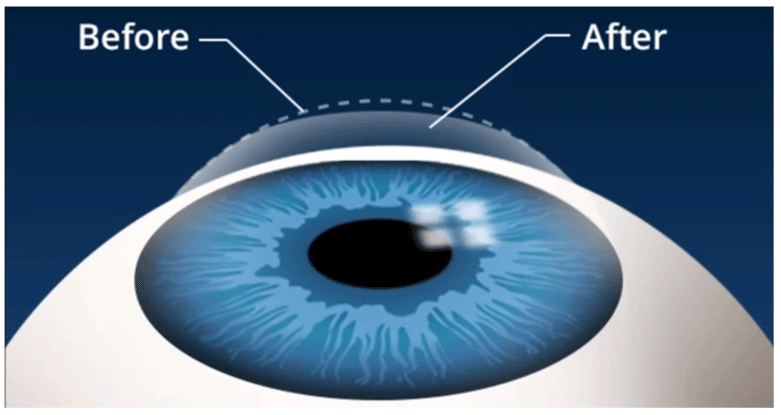
It is the most recent advance in the field of refractive surgery. LASIK is used to reshape the cornea, which is the most powerful lens in the eye. It uses an excimer laser (a cool beam of light) to reshape the cornea and improve vision. The superficial layer of the cornea is raised as a flap and laser is applied to the underlying bed (hence also called as flap and zap). The flap is then replaced.
With the evolution of LASIK now safer procedures are available: FEMTOLASIK and SMILE LASIK . In FEMTO LASIK event the flap is created using a laser and hence there is more predictability and faster healing and less chances of flap displacement. It is also called as bladeless LASIK. SMILE LASIK is also called as Flapless LASIK.
A contact lens is a thin lens placed directly on the surface of the eye. Advancements in contact lens technology offer the potential for successful contact lens wear to most of our patients. Contact lenses not only enhance visual acuity and appearance, but also improve performance in different visual tasks; helps avoid fogging of glasses in different environments, and also improve performance of other fast activities like sports.
Because contact lenses are medical devices placed on the eyes, they require expert fitting and careful instruction, as well as conscientious care and compliance with recommended follow-up examinations to maintain the healthy functioning of your eyes.

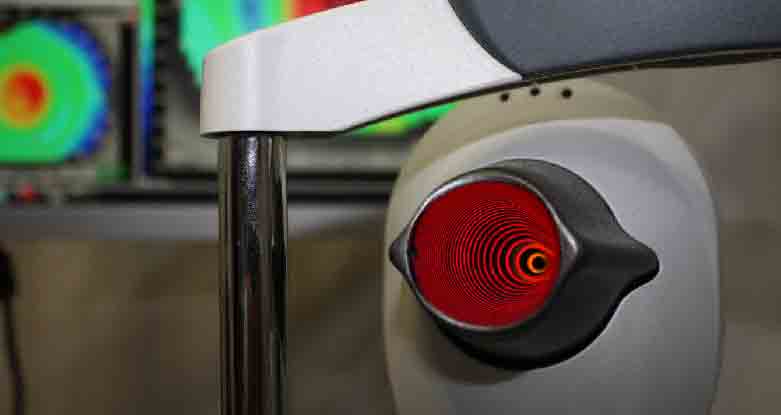
Corneal topography is a computer assisted diagnostic tool that creates a three-dimensional map of the surface curvature of the cornea. An eye with normal vision has an evenly rounded cornea, but if the cornea is too flat, too steep, or unevenly curved, less than perfect vision results. The greatest advantage of corneal topography is its ability to detect irregular conditions invisible to most conventional testing.
Corneal topography produces a detailed, visual description of the shape and power of the cornea. This type of analysis provides your doctor with very fine details regarding the condition of the corneal surface. These details are used to diagnose, monitor, and treat various eye conditions.

The Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery Service focuses on functional disorders of the eyelids, orbit (eye socket), and lacrimal (tear drainage) system, as well as cosmetic enhancement of the area surrounding the eye. It also includes management of tumors around the eye which need specialized care and reconstruction.
Our expertise includes reconstructive and cosmetic eyelid surgery, management of tear drainage disorders, and treatment of orbital diseases, including tumors, inflammation, and thyroid eye disease.

One can’t diagnose diabetic or retinal detachment by looking in the mirror, since your eye will usually look and feel normal. It is a condition caused by diabetes mellitus where blood vessels of the retina are damaged due to the high blood glucose level. Such damage to the blood vessels of the retina can result in abnormal bleeding, swelling of the retina (macular Oedema), poor blood flow to the retina, and/or scarring of the retina.

YAG Laser -
YAG laser capsulotomy is a relatively noninvasive procedure that is used in the treatment of posterior capsular opacification. Posterior capsular opacification is a common long-term complication of cataract surgery that causes decreased vision, glare, and other symptoms similar to that of the original cataract.
Retinal Laser -
Retinal lasers have been specially designed to be able to pass through non-retinal tissue (the lens and cornea) without damaging them. Lasers have become a commonly used and very powerful tool in the treatment of retinal disease. With the help of various lenses, laser beams can be focused on the retina for non-invasive surgical treatment. Most patients have little if any pain following retinal laser surgery. Patients who require more extensive laser may have an ache inside the eye or around the eye. It is suggested to take rest if you have any discomfort after the surgery.

Fundus photography documents the retina, the neurosensory tissue in our eyes which translates the optical images we see into the electrical impulses our brain understands. The retina can be photographed directly as the pupil is used as both an entrance and exit for the fundus camera's illuminating and imaging light rays.
Fundus photographs are visual records which document the current ophthalmoscopic appearance of a patient's retina. They allow the physician to further study a patient's retina, to identify retinal changes on follow-up, or to review a patient's retinal findings with a colleague.